Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking through my links. Learn More
The amount of kWh a generator produces varies based on its capacity. Generators can produce from a few kWh to hundreds of kWh.
Generators are essential for providing backup power during outages or for use in off-grid locations. They come in various sizes and capacities, catering to different needs. Small portable generators might produce 1-2 kWh, ideal for basic household appliances. Larger standby generators can produce 20-48 kWh, sufficient for powering entire homes.
Industrial generators, used in large facilities or construction sites, can generate hundreds of kWh. Choosing the right generator depends on your energy requirements. Understanding your power needs and the generator’s capacity ensures efficient and reliable energy production. Always consult specifications and professional advice before making a purchase.

Introduction To Generator Output
Generators are essential for providing power during outages. They come in different sizes and capacities. Understanding their output is crucial for effective use. This blog post explores how much power a generator can produce.
Importance Of Knowing Output
Knowing a generator’s output helps in choosing the right model. It ensures the generator meets your power needs. It also prevents overloading, which can damage both the generator and connected devices. Understanding output helps in planning for emergencies.
Basic Concepts Of Power Generation
Generators convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. This process involves a motor and alternator. The output is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh).
Here are some key terms:
- Watts (W): Basic unit of power.
- Kilowatts (kW): 1 kW = 1,000 W.
- Kilowatt-hours (kWh): Energy used over time.
A generator’s output depends on its engine and fuel type. A small portable generator may produce 1-3 kWh. Large standby generators can produce 10-20 kWh or more.
Here’s a simple table to illustrate:
| Generator Type | Output (kWh) |
|---|---|
| Portable | 1-3 kWh |
| Standby | 10-20 kWh |
| Industrial | 50+ kWh |
Understanding these basics helps in making informed decisions. Choose a generator that matches your power needs effectively.

Credit: generatorsforexport.com
Factors Influencing Generator Output
Understanding how many kWh a generator produces involves several factors. The generator’s output is influenced by its engine size, fuel type, and efficiency. These elements determine the generator’s performance and reliability.
Engine Size And Efficiency
The engine size plays a crucial role in the generator’s output. A larger engine can produce more power. However, it also consumes more fuel. Efficiency is another key aspect. Efficient engines convert more fuel into electricity. This means less waste and more power.
Let’s look at some typical engine sizes:
| Engine Size (cc) | Approximate Output (kW) |
|---|---|
| 100-200 cc | 1-2 kW |
| 200-400 cc | 2-4 kW |
| 400-700 cc | 4-7 kW |
Smaller engines are suitable for light tasks. Larger engines are for heavy-duty use. Always match the engine size to your power needs.
Fuel Type And Quality
The fuel type affects generator output. Common fuels include gasoline, diesel, and propane. Each fuel type has its pros and cons.
- Gasoline: Easy to find, but less efficient.
- Diesel: More efficient, but harder to store.
- Propane: Clean-burning, but requires special storage.
The fuel quality is just as important. Poor quality fuel can reduce efficiency. It can also damage the engine. Always use the recommended fuel type and quality for your generator.
Read More: Gas vs Propane Generator
Measuring Generator Output
Understanding how to measure a generator’s output is crucial. This helps you determine its efficiency and capacity. Proper measurement ensures your power needs are met without interruption.
Tools And Instruments
To measure a generator’s output, you need the right tools. Some of these tools include:
- Voltmeter: Measures the voltage output.
- Ammeter: Measures the current output.
- Wattmeter: Measures the power output in watts.
These instruments help you get accurate readings. Ensure your tools are in good condition for precise measurements.
Common Measurement Units
Generators produce electricity measured in different units. The most common units include:
- Volts (V): Measures the electrical potential difference.
- Amperes (A): Measures the electrical current.
- Watts (W): Measures the power output.
- Kilowatt-hours (kWh): Measures the energy produced over time.
Understanding these units is key to knowing your generator’s capacity. Use these units to compare different generators easily.
| Tool | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Voltmeter | Voltage | Volts (V) |
| Ammeter | Current | Amperes (A) |
| Wattmeter | Power | Watts (W) |
| Energy Meter | Energy | Kilowatt-hours (kWh) |
Each unit has a specific purpose. Volts and amperes measure instant values. Watts and kilowatt-hours measure total power and energy over time.

Credit: www.eia.gov
Calculating Kilowatt-hours
Understanding how many kilowatt-hours (kWh) a generator produces is key. It helps in planning energy needs and managing costs. This section will cover the basics of calculating kWh. We will break it down into simple steps.
Understanding Kilowatts And Hours
Kilowatts (kW) measure power. Kilowatt-hours (kWh) measure energy use over time. A generator’s power is in kilowatts. To find out energy use, we need both power and time.
If a generator runs at 5 kW, it means it produces 5 kilowatts of power. Running this generator for one hour means it has used 5 kWh of energy.
Sample Calculations
Let’s do some easy calculations:
- Step 1: Find the generator’s power rating in kW.
- Step 2: Determine how many hours the generator runs.
- Step 3: Multiply the power rating by the hours run.
For example, if your generator is rated at 3 kW and it runs for 4 hours, the calculation would be:
3 kW (power) 4 hours (time) = 12 kWh (energy)
So, the generator produces 12 kWh of energy.
Here’s a table for quick reference:
| Generator Power (kW) | Hours Run | Total Energy (kWh) |
|---|---|---|
| 2 kW | 5 hours | 10 kWh |
| 4 kW | 3 hours | 12 kWh |
| 1.5 kW | 6 hours | 9 kWh |
Using these simple steps, you can easily calculate the kWh produced by any generator. This helps in understanding your energy needs and managing fuel costs efficiently.
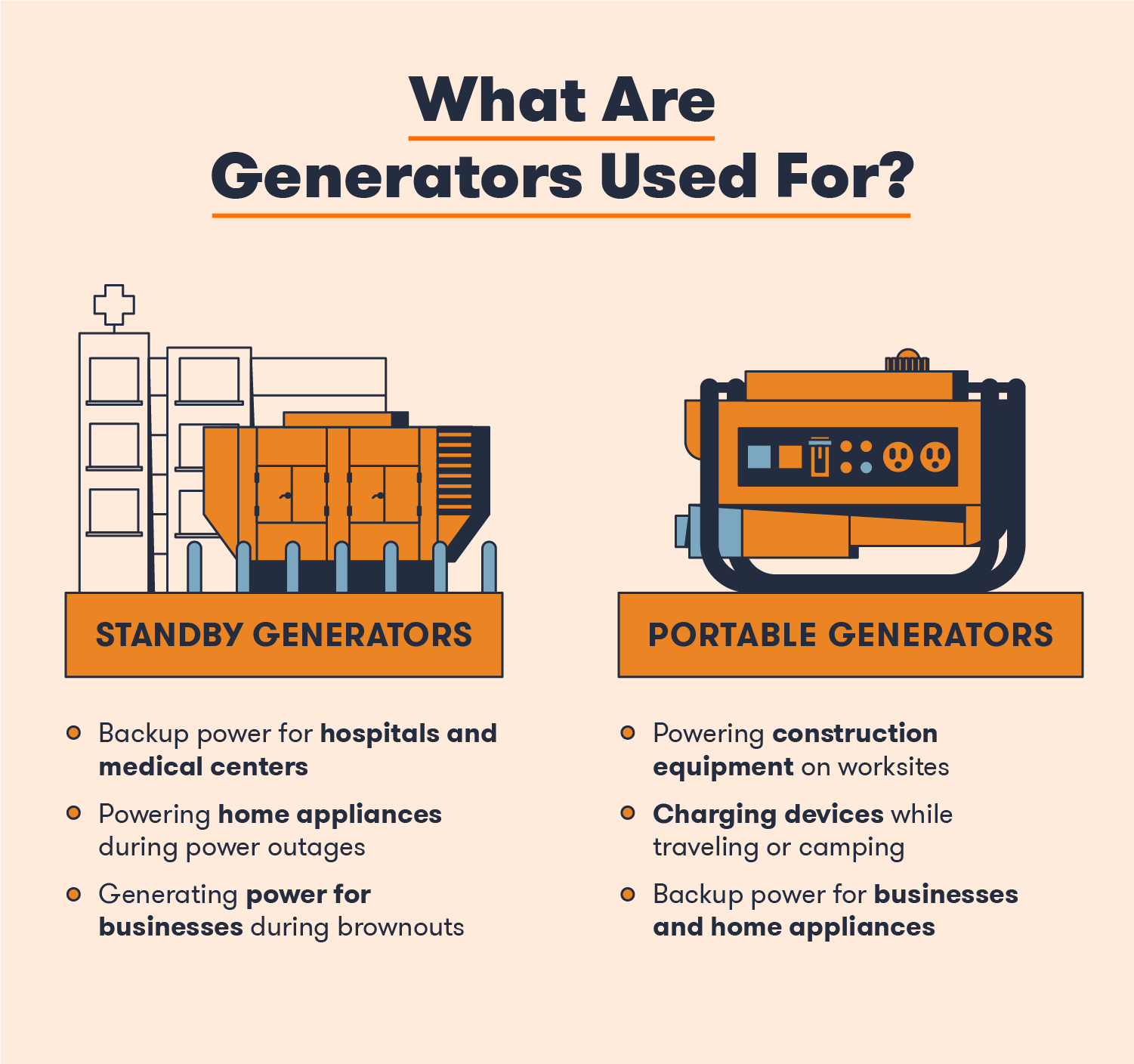
Generator Types And Their Output
Understanding how many kilowatt-hours (kWh) a generator produces depends on its type. Different generators serve various needs and have distinct output levels. Knowing the differences helps in choosing the right generator for your needs.
Portable Generators
Portable generators are small and easy to move. They usually produce between 1,000 and 10,000 watts. This translates to 1 to 10 kWh if the generator runs for an hour. These generators are ideal for small appliances and tools.
- Power output: 1,000 to 10,000 watts
- Use: Outdoor activities, small appliances
Standby Generators
Standby generators are larger and more powerful. They automatically start during a power outage. These generators produce between 7,000 and 20,000 watts, or 7 to 20 kWh per hour. They are perfect for home backup power.
- Power output: 7,000 to 20,000 watts
- Use: Home backup power
Industrial Generators
Industrial generators are the most powerful. They can produce up to several megawatts (MW) of power. For example, a 1 MW generator produces 1,000 kWh in an hour. These generators are used in factories, hospitals, and large buildings.
| Generator Type | Power Output | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Portable Generators | 1,000 to 10,000 watts | Outdoor activities, small appliances |
| Standby Generators | 7,000 to 20,000 watts | Home backup power |
| Industrial Generators | Up to several megawatts | Factories, hospitals, large buildings |
In summary, the output of a generator varies by its type. Whether for a camping trip or powering an entire hospital, there’s a generator to meet every need.
Maximizing Generator Efficiency
Maximizing the efficiency of your generator ensures you get the most power. Efficient use reduces fuel costs and minimizes wear and tear. Let’s explore key strategies to enhance your generator’s performance.
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for keeping your generator in top shape. Schedule periodic checks to inspect and clean essential components. Replace worn-out parts to prevent unexpected breakdowns.
- Check and replace oil regularly.
- Inspect fuel lines for leaks.
- Clean or replace air filters.
- Test battery and electrical connections.
By following these steps, you ensure your generator runs smoothly and efficiently.
Optimal Load Management
Managing the load on your generator optimizes its performance. Avoid overloading, which can strain the engine and reduce efficiency.
- Calculate the total wattage of connected devices.
- Ensure the generator’s capacity matches or exceeds this total.
- Distribute the load evenly across the generator’s output.
Consider using a load management system to automate this process. This helps in maintaining a balanced load and prevents generator overload.
Here’s a simple table to help you understand load distribution:
| Device | Wattage |
|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 600W |
| AC Unit | 1500W |
| Lights | 300W |
Effective load management extends the life of your generator and boosts efficiency.
Real-world Applications
Generators are versatile tools that provide essential power in various situations. Their ability to produce a specific amount of kilowatt-hours (kWh) makes them invaluable in many real-world applications. Below are some key uses of generators.
Home Backup Power
During power outages, home backup generators ensure your house remains functional. They keep the lights on, power essential appliances, and maintain home security systems. Most home generators can produce between 7 kWh to 20 kWh, enough to power critical systems.
| Appliance | Average kWh Usage |
|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 1-2 kWh per day |
| Lights | 0.5-1 kWh per day |
| HVAC System | 3-5 kWh per day |
Construction Sites
Construction sites often lack a stable power source. Portable generators fill this gap by providing the necessary electricity. They power tools like drills, saws, and lighting systems. Typical construction site generators produce between 5 kWh and 30 kWh. This power range supports a variety of equipment.
- Drills: 0.5 kWh per hour
- Saws: 1 kWh per hour
- Lighting: 0.2 kWh per hour
Events And Outdoor Activities
Outdoor events require reliable power for sound systems, lighting, and other equipment. Event generators provide the necessary electricity. These generators usually produce between 3 kWh and 15 kWh. They ensure smooth and uninterrupted event operations.
- Sound Systems: 1-2 kWh per hour
- Lighting: 0.5-1 kWh per hour
- Food Stalls: 0.3-0.7 kWh per hour
Generators bring power to the places where it’s needed most.
Environmental And Economic Impact
Understanding the environmental and economic impact of a generator’s kWh production is crucial. It helps make informed decisions about energy sources. Let’s dive into the key aspects.
Fuel Consumption And Emissions
Generators run on different fuels like diesel, gasoline, and natural gas. Each type has a unique impact on fuel consumption and emissions.
- Diesel Generators: High fuel efficiency, but produce more pollutants.
- Gasoline Generators: Less efficient, with moderate emissions.
- Natural Gas Generators: Cleaner burning, but less energy dense.
Choosing the right fuel can reduce carbon footprint and improve air quality.
Cost-effectiveness Analysis
Evaluating the cost-effectiveness of a generator involves several factors:
- Initial purchase cost
- Fuel costs
- Maintenance expenses
- Operational hours
| Fuel Type | Initial Cost | Fuel Cost | Maintenance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Diesel | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Gasoline | Low | High | High |
| Natural Gas | Moderate | Low | Low |
By examining these factors, you can determine the most cost-effective generator for your needs.
Choosing The Right Generator
Choosing the right generator is crucial for your power needs. You need to consider several factors. This helps you get the best value and performance.
Assessing Your Needs
First, assess your power requirements. List all devices you want to power. Include their wattage in the list. Calculate the total wattage. Ensure your generator can handle this load.
- Lights: 60-100 watts each
- Refrigerator: 600-800 watts
- Television: 100-400 watts
- Computer: 150-300 watts
These are just examples. Check your devices for accurate wattage.
Comparing Brands And Models
Next, compare different brands and models. Look at generators that meet your power needs. Consider their features and prices.
| Brand | Model | Output (kWh) | Price |
|---|---|---|---|
| Brand A | Model X | 5 kWh | $500 |
| Brand B | Model Y | 7 kWh | $700 |
| Brand C | Model Z | 10 kWh | $1000 |
Choose a generator within your budget. Ensure it meets your needs.
Future Trends In Generator Technology
Generators are evolving with new technologies. These trends focus on efficiency, sustainability, and smart technology. Let’s explore future trends in generator technology.
Innovations In Efficiency
New generators are becoming more efficient. They use less fuel and produce more power. This saves money and helps the environment. Advanced engines and better cooling systems are key innovations.
Modern generators also have smart controls. These controls adjust the power output based on demand. This improves efficiency and reduces wear and tear.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Advanced Engines | Higher power output |
| Better Cooling Systems | Longer lifespan |
| Smart Controls | Optimized fuel usage |
Sustainable Power Solutions
Generators are also becoming more eco-friendly. There is a shift towards renewable energy sources like solar and wind. Hybrid generators combine traditional fuel with renewable energy. This reduces carbon emissions.
Biogas generators are another sustainable option. They use organic waste to produce power. This helps manage waste and provides a green energy source.
- Solar Generators
- Wind-Powered Generators
- Hybrid Generators
- Biogas Generators
These trends show a bright future for generator technology. They offer efficient, sustainable, and smart power solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Power Can A Generator Produce?
A generator’s power output varies by model, typically ranging from 500 watts to several megawatts.
What Factors Affect A Generator’s Kwh Output?
Generator size, fuel type, and efficiency directly influence its kilowatt-hour output.
Can Generators Provide Continuous Power?
Yes, many generators are designed for continuous operation, especially industrial and standby units.
How To Calculate A Generator’s Kwh Production?
Multiply the generator’s kW rating by the hours of operation to get kWh production.
Final Words
Understanding how many kWh a generator produces is crucial for managing power needs. It helps in planning energy consumption efficiently. Knowing your generator’s capacity ensures you are prepared for any power outage. Always consider your specific requirements and consult the generator’s manual for accurate information.
This knowledge empowers better energy decisions.


