Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking through my links. Learn More
When it comes to powering your home, RV, or outdoor activities, generators are a popular choice. But not all generators are created equal. The two main types are inverter generators and regular generators, and each has its own unique advantages and disadvantages.
In this article, we’ll take an in-depth look at the key differences between inverter generators and regular generators, so you can decide which one is the best fit for your needs.

What is an Inverter Generator?
An inverter generator is a type of power generator that uses an inverter to convert the AC power it produces into clean, stable DC power, and then back into AC power. This process results in a more consistent, high-quality electrical output compared to a regular generator.
Inverter generators typically use a smaller engine and run at varying speeds, which allows them to adjust their power output based on the electrical load. This makes them more fuel-efficient and quieter than traditional generators.
Advantages of Inverter Generators
Clean Power: Inverter generators produce stable electricity suitable for sensitive devices like laptops, phones, and medical equipment.
Fuel Efficiency: They adjust their engine speed to match the load, using less fuel than regular generators.
Quiet Operation: Most inverter generators operate at a noise level between 50–60 decibels, quieter than a conversation.
Compact and Lightweight: Their smaller design makes them easy to carry and store.
Disadvantages of Inverter Generators
Higher Cost: Inverter generators are generally more expensive than regular generators.
Lower Power Output: They are suitable for smaller loads but may not handle heavy-duty equipment.
What is a Regular Generator?
A regular generator, also known as a conventional generator, is a more basic type of power generator. It produces raw AC power directly from its engine, without any conditioning or conversion. This means the electrical output can be less stable and have more fluctuations in voltage and frequency.
Regular generators usually have a fixed engine speed, so they run at the same RPM regardless of the electrical load. This results in less efficient fuel usage and a louder operation compared to inverter generators.
Advantages of Regular Generators
High Power Output: Regular generators can handle heavy loads, making them ideal for powering large appliances and tools.
Lower Initial Cost: They are more affordable upfront compared to inverter generators.
Durability: Built for extended use, they are reliable in demanding conditions.
Disadvantages of Regular Generators
Noisy Operation: Regular generators typically operate at 70–90 decibels, which can be disruptive.
Fuel Inefficiency: Their engines run at a constant speed, consuming more fuel.
Less Portable: They are larger and heavier, making transportation more difficult.
Inverter Generator vs Regular Generator: Key Differences
Understanding the differences between these two types of generators is essential for making an informed decision. Here’s a comparison:
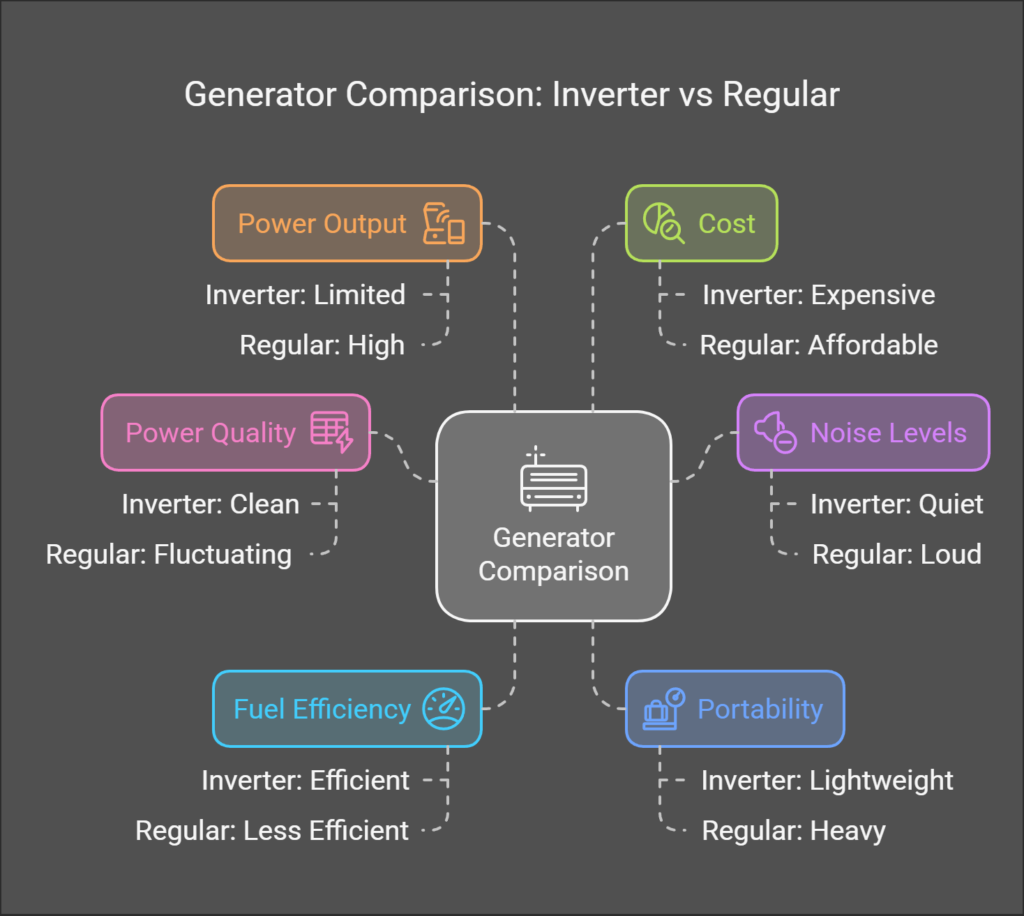
| Feature | Inverter Generator | Regular Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Power Quality | Clean, stable power for electronics | Fluctuating power output |
| Noise Levels | Quiet (50–60 decibels) | Loud (70–90 decibels) |
| Fuel Efficiency | Adjusts engine speed to save fuel | Constant speed, less efficient |
| Portability | Lightweight and compact | Heavy and bulky |
| Power Output | Limited to small appliances | High, suitable for large appliances |
| Cost | Expensive | More affordable upfront |
Now let’s dive into the specific differences between these two generator types:
Power Output Quality
The biggest advantage of an inverter generator is the quality of the power it produces. The inverter circuitry takes the raw AC power from the engine and converts it into clean, stable, pure sine wave AC power. This results in a very consistent voltage and frequency, which is ideal for powering sensitive electronic devices like laptops, phones, and TVs.
In contrast, regular generators produce a more raw, unprocessed form of AC power. This can result in voltage spikes, frequency fluctuations, and harmonic distortion that may not be suitable for delicate electronics. Using a regular generator with sensitive electronics carries a higher risk of damage.
Fuel Efficiency
Inverter generators are generally more fuel-efficient than regular generators. This is because they use a smaller engine that runs at variable speeds, adjusting its output to match the electrical load. The engine only runs at the minimum RPM needed to supply the required power.
Regular generators, on the other hand, have a larger fixed-speed engine that runs at a constant RPM regardless of the load. This means they consume more fuel, even when the power draw is low.
Noise Level
The variable-speed engine and advanced inverter technology in inverter generators make them significantly quieter than regular generators. Most inverter models operate at 50-60 dBA, which is about as loud as a normal conversation.
Regular generators, with their larger fixed-speed engines, typically produce noise levels of 65-85 dBA, which is much louder. This higher noise output can be disruptive in residential areas or when camping/RVing.
Portability and Weight
Inverter generators are generally more portable and lighter weight than regular generators of the same power output. This is because they use smaller engines and require less heavy-duty components.
For example, a 2000-watt inverter generator may weigh around 50 lbs, while a comparable regular generator could weigh 80 lbs or more. The lighter weight and compact size of inverter generators make them easier to move, transport, and store.
Surge Capacity
When it comes to surge capacity, regular generators typically have the advantage. Surge capacity refers to the generator’s ability to handle brief power spikes or surges, which are common when starting up electric motors or other high-wattage appliances.
Regular generators, with their larger engines and alternators, can often provide significantly more surge capacity than similarly-sized inverter models. This makes them better suited for powering tools, pumps, air conditioners, and other devices with high startup wattage requirements.
Cost
Generally speaking, inverter generators tend to be more expensive than regular generators of the same power output. This is due to the more advanced inverter technology and electronic components required.
A good quality 2000-watt inverter generator may cost $800-$1,200, while a comparable regular generator could be purchased for $500-$800. The higher initial cost of an inverter generator is often offset by the fuel savings and quieter operation over time.
Use Cases for Inverter and Regular Generators
Now that we’ve covered the key differences, let’s look at some common use cases for each type of generator:
Inverter Generators
Powering Sensitive Electronics: Inverter generators are ideal for powering laptops, phones, TVs, and other delicate electronics due to their clean, stable power output. The regulated sine wave voltage protects these devices from damage.
Camping and RVing: Inverter generators are popular choices for camping, tailgating, and RV use. Their quiet operation and lightweight, compact design make them easy to transport and use in close quarters.
Backup Home Power: Many homeowners use inverter generators as backup power sources during outages. Their fuel efficiency means they can run for longer on a single tank of gas.
Regular Generators
High-Wattage Applications: Regular generators excel at powering high-wattage devices and appliances that require a lot of startup power, such as power tools, pumps, air conditioners, and refrigerators.
Rugged Jobsites: The heavy-duty construction and surge capacity of regular generators make them well-suited for use on construction sites, farms, and other rugged work environments.
Whole-Home Backup Power: Larger regular generators are often used as whole-house backup power systems, providing enough capacity to power an entire home during an outage.
Choosing Between an Inverter and Regular Generator
So, which type of generator is the best choice for you? It really depends on your specific power needs and usage requirements. Here are some factors to consider:
Power Needs
If you primarily need to power sensitive electronics, an inverter generator is likely the better option. The clean, stable power output will protect your devices from damage.
However, if you need to power high-wattage appliances or tools with significant startup requirements, a regular generator may be a better fit due to its higher surge capacity.
Noise and Fuel Efficiency
If noise level is a major concern, such as when camping or using the generator near your home, an inverter generator’s quiet operation is a big advantage.
And if fuel efficiency is important, the variable-speed engine in an inverter generator will typically provide better fuel economy than a regular generator.
Portability and Weight
For applications where you need to regularly move or transport the generator, the lighter weight and more compact size of an inverter model can be very beneficial, such as when camping or tailgating.
Budget
Inverter generators do tend to cost more upfront than regular generators of the same power output. If budget is a primary concern, a regular generator may be the more affordable option.
Ultimately, the best generator for you will depend on your specific power needs, usage environment, and personal preferences. Consider your priorities and make the choice that fits your requirements the best.
Final Words
Both inverter generators and regular generators have their own unique strengths and weaknesses. Inverter generators excel at providing clean, efficient power for sensitive electronics and quiet operation, while regular generators offer higher surge capacity and are often more affordable.
When choosing between the two, carefully assess your power needs, noise tolerance, portability requirements, and budget. This will help you select the generator type that is the best match for your particular applications and needs.
Regardless of which generator you choose, make sure to follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper operation, maintenance, and safety. With the right generator, you can keep your devices, tools, and essential home systems powered up, even when the grid goes down.
FAQs
Are inverter generators more fuel-efficient than regular generators?
Yes, inverter generators are generally more fuel-efficient. They use a variable-speed engine that adjusts its output to match the electrical load, only running at the minimum RPM needed. Regular generators have a larger fixed-speed engine that consumes more fuel even when the power draw is low.
How much quieter are inverter generators compared to regular generators?
Inverter generators are significantly quieter than regular generators. Most inverter models operate at 50-60 dBA, which is about as loud as a normal conversation. In contrast, regular generators typically produce noise levels of 65-85 dBA, which can be quite disruptive, especially in residential areas or when camping.
Are inverter generators more portable than regular generators?
Yes, inverter generators tend to be more portable and lighter weight than regular generators of the same power output. This is because they use smaller engines and require less heavy-duty components. For example, a 2000-watt inverter generator may weigh around 50 lbs, while a comparable regular generator could weigh 80 lbs or more.
Which type of generator is better for powering sensitive electronics?
Inverter generators are the better choice for powering sensitive electronics like laptops, phones, and TVs. The clean, stable sine wave power they produce protects these delicate devices from the voltage spikes and harmonic distortion that can occur with the raw AC output of regular generators.
Which generator is better for camping?
Inverter generators are better for camping due to their quiet operation, lightweight design, and ability to power small devices efficiently.