Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking through my links. Learn More
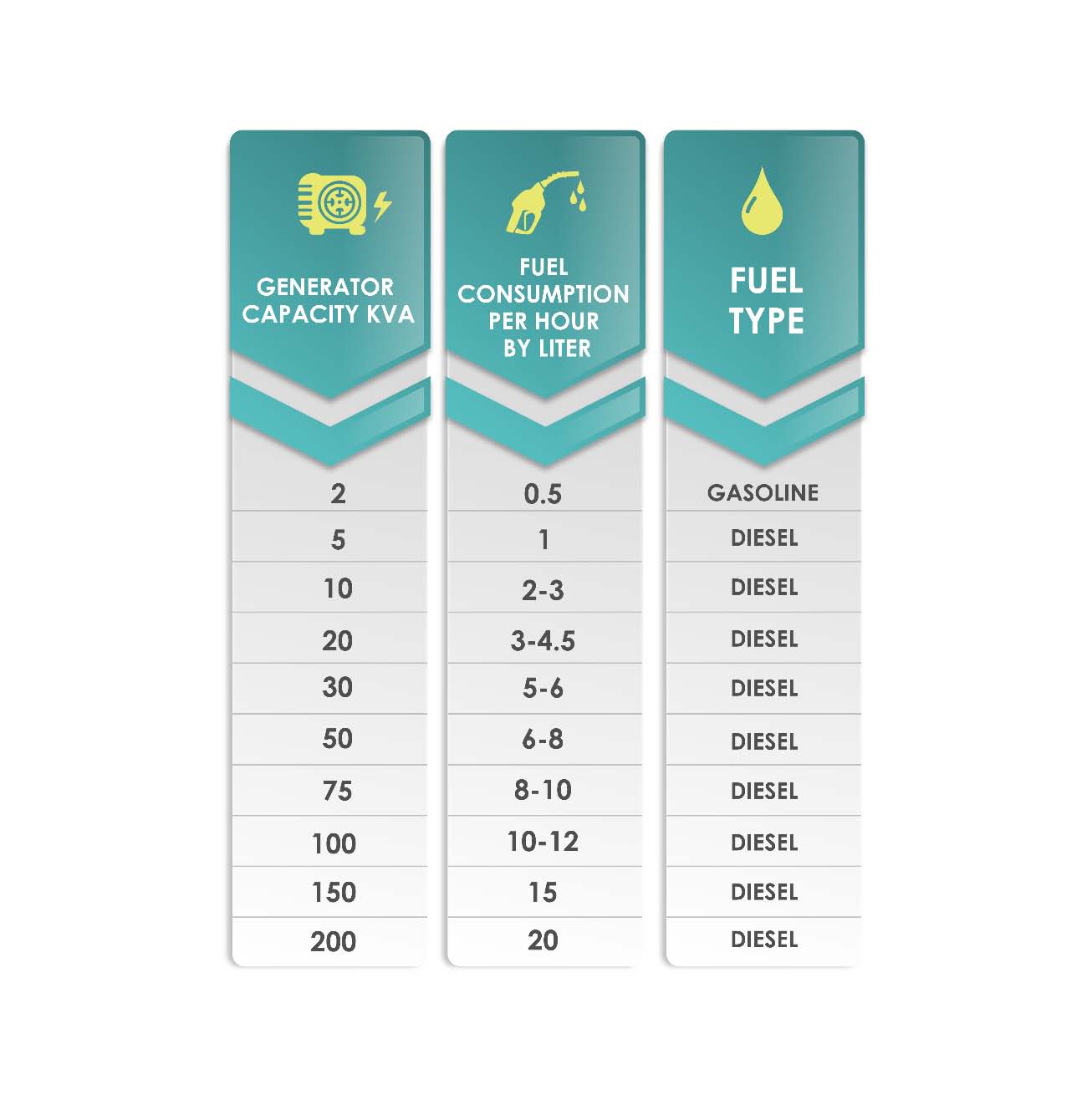
A diesel generator typically uses between 0.4 to 0.9 gallons per hour, depending on its size and load. Smaller generators consume less fuel compared to larger ones.
Diesel generators are crucial for backup power in many industries and homes. Understanding their fuel consumption helps in planning and budgeting. Diesel efficiency varies based on generator size, load capacity, and operational hours. Smaller units generally use less fuel, making them suitable for light tasks.

Larger generators, while consuming more, can power extensive systems. Regular maintenance ensures optimal fuel efficiency. Knowing these details aids in choosing the right generator for your needs. Efficient fuel usage not only saves money but also extends the generator’s lifespan. Proper management of diesel consumption is essential for sustainable and cost-effective operation.
Factors Influencing Diesel Consumption
Understanding how much diesel a generator uses per hour is essential. Various factors can affect diesel consumption. Let’s explore these factors in detail.
Generator Size
The size of the generator plays a crucial role. Larger generators consume more diesel. Smaller generators use less fuel. Check the generator’s power rating. Higher ratings mean higher fuel consumption.
Load Capacity
Load capacity impacts diesel usage significantly. Running a generator at full load uses more fuel. Partial loads consume less diesel. Always match the load with the generator’s capacity. Overloading can increase fuel consumption and cause damage.
Fuel Quality
The quality of diesel fuel matters. High-quality fuel ensures efficient combustion. Poor-quality fuel can lead to higher consumption. Regularly check and maintain fuel quality. Using additives can improve fuel efficiency.
| Factor | Impact on Diesel Consumption |
|---|---|
| Generator Size | Large generators consume more diesel |
| Load Capacity | Full loads use more fuel |
| Fuel Quality | High-quality fuel ensures efficient combustion |
- Regular maintenance can improve fuel efficiency.
- Monitor fuel levels frequently.
- Consider the generator’s environment for optimal performance.
Calculating Diesel Usage
Understanding how much diesel a generator uses per hour is crucial for budgeting and efficiency. Calculating diesel usage involves a few simple steps. This can help you estimate fuel costs and manage resources effectively.
Basic Formula
The basic formula to calculate diesel usage is straightforward. You need to know the generator’s load and fuel consumption rate.
- Load: The electrical power the generator produces, measured in kilowatts (kW).
- Fuel Consumption Rate: The amount of diesel consumed per hour, measured in liters per hour (L/h).
Use this formula:
Diesel Usage (L/h) = Load (kW) × Fuel Consumption Rate (L/h per kW)
Example Calculations
Let’s look at some example calculations to make it clearer.
Example 1:
- Load: 10 kW
- Fuel Consumption Rate: 0.25 L/h per kW
Using the formula:
Diesel Usage = 10 kW × 0.25 L/h per kW = 2.5 L/h
The generator uses 2.5 liters of diesel per hour.
Example 2:
- Load: 20 kW
- Fuel Consumption Rate: 0.3 L/h per kW
Using the formula:
Diesel Usage = 20 kW × 0.3 L/h per kW = 6 L/h
The generator uses 6 liters of diesel per hour.
| Load (kW) | Fuel Consumption Rate (L/h per kW) | Diesel Usage (L/h) |
|---|---|---|
| 10 | 0.25 | 2.5 |
| 20 | 0.3 | 6 |
Impact Of Load On Fuel Consumption
Understanding how much diesel a generator uses per hour depends on the load. The load significantly impacts fuel consumption. Generators run more efficiently under specific conditions.
Full Load Vs Partial Load
Fuel consumption varies between full load and partial load. At full load, a generator uses fuel at its maximum rate. For example, a 10 kW generator consumes about 2.5 liters of diesel per hour at full load.
Partial load changes this dynamic. Running at 50% load, the same generator may consume around 1.5 liters per hour. This means partial load can save fuel, but efficiency varies.
| Load Level | Fuel Consumption (liters/hour) |
|---|---|
| Full Load (100%) | 2.5 |
| Partial Load (50%) | 1.5 |
Efficiency Considerations
Efficiency is crucial. Generators are designed to run at optimal efficiency under specific loads. Running a generator at full capacity ensures it operates at peak efficiency.
Partial load can decrease efficiency. This happens because generators are less efficient below their optimal operating range. The generator engine may burn more fuel per kW produced at lower loads.
- Full load ensures maximum efficiency.
- Partial load reduces fuel consumption but may lower efficiency.
Maintaining a balance between load and efficiency is key. Regular maintenance also helps improve fuel efficiency.
Improving Fuel Efficiency
Improving the fuel efficiency of a diesel generator is essential. It saves money and reduces environmental impact. This guide will discuss key strategies. Let’s dive into the specifics.
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance ensures your generator runs smoothly. Clean filters and replace them on time. Check the oil levels and change them as needed. Inspect the fuel system for leaks. A well-maintained generator uses less fuel.
Optimal Load Management
Managing the load on your generator is crucial. Avoid running the generator at low loads. Low loads can cause inefficiency and higher fuel consumption. Aim for 70-80% of the generator’s capacity. This range is the most efficient.
| Load Level | Fuel Efficiency |
|---|---|
| 0-30% | Poor |
| 30-70% | Moderate |
| 70-80% | Optimal |
| 80-100% | Good |
- Keep the generator clean.
- Ensure proper ventilation.
- Use high-quality diesel.
Comparing Diesel Generators To Alternatives
Choosing the right generator depends on various factors. Diesel generators are popular, but it’s important to compare them with other types. Understanding the differences can help you make an informed choice.
Gasoline Generators
Gasoline generators are common and easy to find. They are usually cheaper than diesel generators. Gasoline is widely available, making refueling convenient. But gasoline generators have some drawbacks.
- Shorter lifespan compared to diesel generators.
- Higher fuel consumption.
- More frequent maintenance required.
Gasoline generators are ideal for short-term use. They are best for small projects or emergency power needs.
Natural Gas Generators
Natural gas generators use natural gas as fuel. They are more environmentally friendly than diesel and gasoline generators. Natural gas is a clean-burning fuel, reducing harmful emissions.
| Feature | Natural Gas Generators | Diesel Generators |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel Availability | Depends on pipeline access | Widely available |
| Fuel Storage | No need for storage | Requires storage tanks |
| Emissions | Lower emissions | Higher emissions |
Natural gas generators are great for continuous use. They are suitable for homes and businesses with natural gas access.
Read More: Gas vs Propane Generator

Real-world Usage Scenarios
Understanding how much diesel a generator uses per hour is crucial. It helps in budgeting and planning for fuel needs. Let’s explore some real-world usage scenarios for residential and commercial settings.
Residential Use
In homes, generators are often used during power outages. The diesel consumption varies depending on the generator size and load. For a small household generator, the consumption can be around 0.5 to 1 gallon per hour.
| Generator Size | Load | Diesel Consumption (per hour) |
|---|---|---|
| 5 kW | 50% | 0.5 gallons |
| 10 kW | 75% | 1 gallon |
Commercial Use
In commercial settings, generators support large equipment and systems. They often run for extended periods. The diesel consumption is higher compared to residential use. A commercial generator might consume between 3 to 10 gallons per hour.
- A 50 kW generator at 50% load: 3 gallons per hour.
- A 100 kW generator at 75% load: 7 gallons per hour.
- A 200 kW generator at full load: 10 gallons per hour.
For businesses, calculating fuel needs is essential. It helps maintain operations smoothly without unexpected fuel shortages.

Frequently Asked Questions
How Much Diesel Does A Generator Use?
A generator typically uses 0. 5 to 3 gallons of diesel per hour, depending on its size and load.
What Factors Affect Generator Diesel Consumption?
Diesel consumption depends on generator size, load, efficiency, and fuel quality. Larger loads and less efficient models use more fuel.
How Can I Reduce Diesel Usage?
Reduce diesel usage by maintaining the generator, using energy-efficient devices, and ensuring the generator operates at optimal load.
Is Diesel Generator More Efficient Than Gas?
Diesel generators are generally more efficient and durable than gas generators, offering better fuel economy and longer lifespan.
Conclusion
Understanding diesel consumption helps in budgeting and efficient generator use. Calculate your generator’s hourly fuel usage accurately. Proper maintenance ensures optimal performance and fuel efficiency. Always consult your generator’s manual for specific details. Stay informed to make smart decisions and save on fuel costs.