Disclosure: This post contains affiliate links and I will be compensated if you make a purchase after clicking through my links. Learn More
Picking the right generator size is key to keeping your power needs met. If you’ve ever tried to choose a generator, you know it’s not always easy. Without the right math, you might end up with a generator that’s too small or too big for what you need. That’s where a generator Size calculator comes in handy. It’s a simple tool that helps you figure out exactly what size generator do you need.

Understanding Generator Sizing
Why Generator Size Matters
Choosing the wrong generator size can cause problems. If your generator is too small, it won’t power all your stuff. This can lead to overloading, which might damage your generator or the things you’re trying to power. It could even shut down when you need it most.
On the flip side, a generator that’s too big wastes fuel and money. It costs more upfront and burns more fuel than you need. This means you’ll spend more on gas or propane over time. Plus, running a generator at low loads for long periods can cause issues like wet stacking in diesel generators, which can hurt the engine.
The right size generator runs more efficiently. It uses less fuel and lasts longer because it’s not working too hard or too little. This saves you money on both fuel and repairs in the long run.
Factors Affecting Generator Size
When figuring out what size generator do you need, think about these things:
Continuous vs. Peak Power Needs:
- Continuous power is what your appliances use all the time.
- Peak power is the extra juice some appliances need when they start up.
- Your generator needs to handle both, especially the peak power for things like fridges or air conditioners that use more power to get going.
Types of Appliances and Devices:
- Make a list of everything you want to power.
- Look at both how much power each thing uses normally and how much it needs to start.
- Don’t forget about small stuff like phone chargers or lamps – it all adds up.
Where You Live and the Weather:
- If you live somewhere hot, you might need more power for cooling.
- In cold places, you might need extra power for heating.
- Some areas have rules about generator noise, which might affect your choice.
By thinking about these factors, you can get a good idea of what size generator do you need. This helps you pick a generator that’s just right – not too big, not too small.
How to Use the Generator Sizing Calculator
A generator size calculator is a handy tool that takes the guesswork out of choosing the right size generator. By using this calculator, you can ensure that your generator will meet your power needs without wasting fuel or money on unnecessary capacity. Let’s walk through the process of using our generator size calculator effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide to Generator Sizing
The first step in using our generator size calculator is to create a comprehensive list of all the appliances and devices you plan to power. This list should include everything from large appliances like refrigerator air conditioners to smaller items such as lamps, phone chargers, and televisions. Don’t overlook any electrical items, as even small devices contribute to your total power needs.
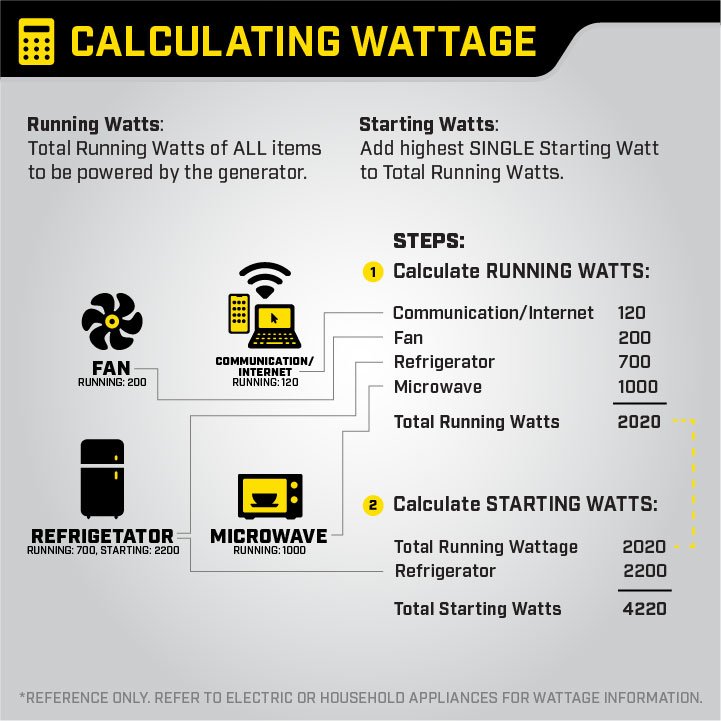
Once you have your list, the next step is to determine the wattage requirements for each item. This involves finding two important numbers: the running watts and the starting watts. Running watts represent the power an appliance uses during normal operation, while starting watts are the extra power some devices need when they first turn on. Motors, particularly those in refrigerators, air conditioners, and power tools, often require significantly more starting watts than running watts.
To find these wattage values, start by checking the appliance itself. Many devices have a label or plate that lists their power consumption. If you can’t find this information on the appliance, check owner’s manual or manufacturer’s website. For appliances that only list amperage, you can calculate the wattage by multiplying the amps by the voltage (typically 120 volts for standard household outlets).
Watts = Volts x Amps.
After gathering all the necessary wattage information, it’s time to input these values into the generator size calculator. Our calculator will have fields for you to enter both the running and starting watts for each appliance. Be sure to fill in all the fields accurately to get the most precise results.
The final step is interpreting the results (Show Details) provided by the calculator. The calculator will typically give you a required running watts and starting watts figure, which represents the size of generator you need to power all your listed appliances simultaneously. This number takes into account both the total running watts of all your devices and the highest starting watt requirement among them.
Generator Size Calculator
Enter the quantity for each device your generator will power, then click Calculate Wattage. The calculator will display the total starting and running watts. When you click the Show Details button, you will see the minimum generator size with starting watts.
| Item | Running Watts | Starting Watts | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smartphone | |||
| Tablet | |||
| WiFi Router | |||
| CPAP | |||
| Radio/Speaker | |||
| Drone | |||
| Laptop Computer | |||
| Television | |||
| Game Console | |||
| Desktop Computer | |||
| Satellite Receiver |
| Item | Running Watts | Starting Watts | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electric Cooler | |||
| Air Pump | |||
| Cabin lights | |||
| Water pump | |||
| Anchor winch | |||
| Bilge pump | |||
| 15000BTU A/C |
| Item | Running Watts | Starting Watts | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fan | |||
| Handheld Vacuum | |||
| RV Fridge | |||
| Slow Cooker | |||
| Coffee Maker | |||
| Microwave | |||
| Radiant Heater | |||
| Water Heater | |||
| Electric range (1 element) | |||
| 11000BTU A/C | |||
| 13000BTU A/C | |||
| 15000BTU A/C |
| Item | Running Watts | Starting Watts | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Light bulb (LED) | |||
| Curling iron | |||
| Slow Cooker | |||
| Refrigerator | |||
| Deep freezer | |||
| Microwave oven | |||
| Coffeemaker | |||
| Sump pump | |||
| Air conditioner – Window | |||
| Portable electric heater | |||
| Electric range (1 element) |
| Item | Running Watts | Starting Watts | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dishwasher | |||
| Garage door opener | |||
| Vacuum cleaner | |||
| Dehumidifier | |||
| Furnace fan | |||
| Washing machine | |||
| Hair dryer | |||
| Submersible pump (1HP) | |||
| Water heater | |||
| Air conditioner – Central | |||
| Clothes dryer (electric) |
| Item | Running Watts | Starting Watts | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| String Lights | |||
| Box Fan | |||
| Small Appliances | |||
| Bouncy Castle Fan (1HP) | |||
| Event Speakers | |||
| Popcorn Machine |
| Item | Running Watts | Starting Watts | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drill Charger | |||
| Jigsaw | |||
| Orbital Sander | |||
| Small Air Compressor | |||
| Hand Drill | |||
| Angle Grinder | |||
| Impact wrench ½” | |||
| Belt sander | |||
| Chainsaw | |||
| Router | |||
| Chop Saw | |||
| Disk Sander |
| Item | Running Watts | Starting Watts | Quantity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chick brooder | |||
| Milk pump | |||
| Milking machine | |||
| Feed grinder | |||
| Electric fence |
| Item | Running Watts | Starting Watts | Quantity | Actions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Note: Keep in mind, results are estimates and may vary due to real-world conditions.
Tips for Accurate Generator Size Calculations
- Check appliance tags or manuals for exact wattage info.
- Use online wattage guides for common items if you can’t find the exact numbers.
- Don’t forget about startup power – some things need extra watts to get going.
- Add up both the running watts and the highest starting watts to get your total.
- Round up your final number to be safe – it’s better to have a little extra power than not enough.
For a better understanding, see the visual image.
Types of Generators and Their Wattage Ranges
Understanding different generator types and their wattage ranges helps you match your power needs to the right equipment. Let’s explore the main types of generators and their characteristics.
Portable Generators: Versatile Power on the Go
Portable generators offer flexibility for various uses, typically ranging from 1,000 to 10,000 watts.
- Small portable generators (1,000-2,000 watts): Ideal for camping or powering a few small appliances during outages. Lightweight and easy to transport.
- Mid-range models (3,000-5,000 watts): Suitable for RV use, tailgating, or as emergency home backup. Can run a refrigerator, lights, and smaller appliances.
- Larger portable generators (6,000-10,000 watts): Can power essential home circuits during outages, including well pumps and heating systems.
Portable generators usually run on gasoline, with some offering propane or dual-fuel options. They’re affordable and don’t require professional installation, making them popular for occasional or emergency use.
Standby Generators: Whole-House Power Solutions
Standby generators provide top-tier residential backup power, typically ranging from 5,000 to 20,000 watts.
- 5,000-10,000 watts: Can power essential home circuits, including refrigerators, heating/cooling systems, and basic electronics.
- 12,000-20,000 watts: Suitable for larger homes or powering most/all electrical appliances during outages.
These generators connect to your home’s electrical system and fuel source (natural gas or propane). They start automatically during power outages, providing seamless transition and minimal disruption. While they require professional installation, standby generators offer peace of mind for areas prone to frequent or extended power outages.
Inverter Generators: Clean Power for Sensitive Electronics
Inverter generators, ranging from 1,000 to 4,000 watts, produce stable, high-quality electricity safe for sensitive electronics.
- Small inverter generators (1,000-2,000 watts): Extremely portable and quiet, perfect for camping or powering small RV appliances.
- Larger models (3,000-4,000 watts): Can handle RV air conditioners, multiple household appliances, or several power tools.
Inverter technology allows these generators to adjust engine speed based on power demand, improving fuel efficiency and reducing noise. While more expensive than standard portable generators, they excel in situations requiring clean power or low noise levels.
By understanding these generator types and their wattage ranges, you can better match your calculated power needs to the right generator. Whether you need a small unit for camping, a whole-house standby system, or a quiet inverter generator for your RV, there’s a generator to fit your specific requirements.
Calculating Generator Size for Specific Scenarios
When it comes to choosing the right generator size, different scenarios call for different approaches. Whether you’re looking to power your entire home during an outage or need portable power for outdoor activities, understanding your specific needs is crucial. Let’s explore how to calculate generator size for various common situations.
What Size Generator Do I Need for My House?

Determining the right generator size for your home depends on several factors, including the size of your house, the number of appliances you want to power, and your overall energy consumption. While our generator size calculator can give you precise figures, it’s helpful to understand some general guidelines.
For a small home or to power just essential circuits, a generator in the 3,000 to 6,500-watt range might be sufficient. This size can typically handle basics like your refrigerator, freezer, some lights, and a few small appliances. It’s enough to keep your food cold, maintain some lighting, and perhaps run a fan or space heater, depending on the season.
A medium-sized home or those wanting more comfort during an outage might need a generator in the 6,500 to 12,000-watt range. This size can power everything in a small home setup, plus additional appliances like a water heater, washing machine, or a window air conditioner. With this range, you can maintain a good level of comfort during extended power outages.
For larger homes or those wanting to maintain full power during an outage, a generator in the 12,000 to 20,000-watt range is often necessary. This size can handle most or all of a typical home’s electrical needs, including power-hungry appliances like electric dryers, electric stoves, and central air conditioning systems.
To get a more accurate estimate for your specific home, it’s important to calculate the wattage of your essential appliances. Here are some common household items and their typical wattage requirements:
- Refrigerator: 600-800 watts
- Freezer: 500-700 watts
- Sump pump: 750-1,500 watts
- Well pump: 1,000-2,000 watts
- Furnace fan: 500-800 watts
- Window air conditioner: 1,000-1,500 watts
- Central air conditioner: 2,000-4,000 watts
- Electric water heater: 3,000-4,000 watts
- Lights: 60-600 watts (depending on type and number)
- Microwave: 600-1,200 watts
- Television: 100-400 watts
- Computer: 200-400 watts
Remember, these are average figures, and your actual appliances may vary. Always check the specific wattage of your appliances for the most accurate calculations.
When using our generator size calculator for your home, don’t forget to account for startup power. Some appliances, particularly those with motors like refrigerators and air conditioners, require extra power to start up. This surge can be two to three times their running wattage and needs to be factored into your calculations.
Generator Sizing for Outdoor Activities and Job Sites
Different outdoor activities and work environments have varying power needs. Let’s break down some common scenarios:
Camping and Small Outdoor Events (1,000 – 2,000 watts): For basic camping needs or small outdoor gatherings, a small portable generator in the 1,000 to 2,000-watt range is often sufficient. This size can power essentials like:
- LED lighting for your campsite
- Charging stations for phones and tablets
- A small electric cooler or mini-fridge
- Portable fans or heaters, depending on the weather
- Small cooking appliances like a coffee maker or electric griddle
These smaller generators are lightweight and quiet, making them ideal for campgrounds where noise regulations may be in place.
Tailgating and RVing (2,000 – 4,000 watts): Tailgating parties and RV trips often require a bit more power. A generator in the 2,000 to 4,000-watt range can handle:
- A television and sound system for game day entertainment
- Portable refrigerator or large cooler
- Electric grill or other cooking appliances
- Lighting systems
- RV air conditioner (usually requires at least 2,000-3,000 watts)
- Various chargers and small appliances
For RV use, inverter generators are particularly popular due to their clean power output, which is safe for sensitive electronics, and their typically quieter operation.
Construction and Job Sites (5,000 – 15,000 watts): Construction sites and other job locations often need substantial power to run various tools and equipment. The exact size depends on the specific tools being used, but a range of 5,000 to 15,000 watts is common. This size range can typically handle:
- Multiple power tools (circular saws, drills, etc.)
- Compressors
- Welding equipment
- Work lights
- Heating or cooling equipment
When calculating generator size for a job site, it’s crucial to consider which tools will be used simultaneously and account for the high starting watts of many power tools.
Additional Factors to Consider in Generator Sizing
When using generator sizing calculator or estimating your power needs, there are several additional factors to keep in mind:
Altitude: Generators may lose efficiency at higher altitudes. If you’re operating above 3,000 feet, you might need to increase your estimated wattage needs by about 3.5% for every 1,000 feet above sea level.
Temperature: Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can affect generator performance. In very hot conditions, you might need a slightly larger generator to compensate for decreased efficiency.
Future Needs: Consider any potential increases in your power requirements. Are you planning to add new appliances or expand your living space? It might be worth sizing up slightly to accommodate future needs.
Run Time: Think about how long you need the generator to run without refueling. Larger generators typically have bigger fuel tanks and can run longer between refills.
Portability vs. Power: For outdoor activities and job sites, there’s often a trade-off between power output and portability. Consider how often you’ll need to move the generator and choose a size that balances your power needs with practical mobility.
Electrical Codes and Regulations: Some areas have specific requirements for generator installations, particularly for whole-house standby generators. Always check local regulations when sizing a generator for your home.
Fuel Availability: In extended outage situations, consider how easily you can obtain fuel for your generator. This might influence your choice between gasoline, propane, or diesel models.
By taking these factors into account and using a reliable generator sizing calculator, you can ensure that you select a generator that not only meets your current needs but also serves you well in various scenarios and conditions.
Remember, while it’s possible to get by with a smaller generator by carefully managing your loads, it’s generally better to have slightly more capacity than you think you need. This provides a safety margin and allows for unexpected power requirements. A properly sized generator ensures you have the power you need, when you need it, without wasting fuel or overworking your equipment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between running watts and starting watts?
Running watts are the power appliances use when they’re on and running normally. Starting watts are the extra power some appliances need for a few seconds when they first turn on. Motors in things like fridges, air conditioners, and power tools often need more starting watts. Your generator needs to handle both. Read more in details.
How do I determine the wattage of appliances not listed on your calculator?
Look for a label on the appliance that shows watts or amps. If it shows amps, multiply by volts (usually 120) to get watts. You can also check the user manual or the manufacturer’s website. For unlisted appliances, search online for “wattage of [appliance name]” to find typical values.
Can I use a smaller generator if I manage my loads carefully?
Yes, you can use a smaller generator by managing what you power. Don’t run all appliances at once. Turn on high-wattage items one at a time. Use energy-efficient appliances. Plan which items are most important to power during an outage. This smart use can let you get by with a smaller, more affordable generator.
How often should I reassess my generator size needs?
Check your generator size needs every few years or when you make big changes to your home or power usage. New appliances, home additions, or changes in how you use power can affect your needs. Also, reassess if you find your current generator struggling to keep up or if it’s often running with a very light load.
Wrap-Up
Picking the right size generator is key to meeting your power needs effectively. Our generator size calculator helps make this choice easier. Remember these main points:
- List all the items you need to power
- Find both running and starting watts for each
- Consider where and how you’ll use the generator
- Think about fuel type, noise, and environmental factors
By using the calculator and keeping these factors in mind, you’ll be well-equipped to choose a generator that fits your needs perfectly. Whether it’s for home backup, outdoor fun, or work sites, the right generator keeps your power flowing when you need it most.
Ready to find your ideal generator size? Try our generator size calculator now and take the guesswork out of your decision. With the right information, you can power up with confidence!